Summary
Polymatech Electronics Limited is a rapidly scaling, capital-intensive semiconductor manufacturer aligned with India’s localization push, supported by strong manufacturing capabilities, vertical integration, and expansion into high-value segments such as medical devices and GaN chips. While the company has delivered exceptional revenue growth driven by capacity expansion, rising working capital needs, margin pressure, and execution risks remain key challenges. Overall, Polymatech offers meaningful long-term growth potential, but its investment appeal is best suited for high-risk-tolerant, long-term investors rather than short-term or conservative participants.
Company Overview
The company Polymatech Electronics Limited is a semiconductor manufacturer located in India that operates under the brand "The Semiconductor People." Founded in 2007, Polymatech has its corporate headquarters in the state of Tamil Nadu at the SIPCOT Hi-Tech Special Economic Zone. This location is at the centre of electronics and advanced manufacturing in the country.
As an integrated designer and manufacturer of semiconductor chips and LED light source products, Polymatech operates in all aspects of the semiconductor value chain, such as manufacturing, packaging, and materials-oriented innovation. This operating model distinguishes Polymatech from fabless and pure design companies in the semiconductor market and gives the company the ability to better meet global demand cycles and embrace the strategic thrust of the Indian government to localise the semiconductor industry through import substitution.
Polymatech's operating model is characterised by high asset intensity and production-centric operation. The manufacturing operations are designed around cleanroom infrastructure, advanced production equipment, and, increasingly, automated systems. Polymatech is embedding AI, IoT, robotics, and digital twin technologies to improve yield optimisation, minimize unplanned downtime, and increase energy efficiencies that drive the competitive advantages of semiconductor manufacturing.
Polymatech is strategically moving away from a manufacturing-focused entity to a full-fledged trading company by adding trading and importing/exporting semiconductor manufacturing equipment and electronic component sales to its offerings. This is designed to expand the scope of Polymatech's activities as a participant in the electronic supply chain and increase the strength of the company's supply chain by enhancing communication with global OEMs.
Polymatech operates under a defined governance process through an active board of directors and specialised committees, and has established a global presence through its subsidiaries in Singapore, the USA, Bahrain, and India.
Business segment
Polymatech focuses primarily on manufacturing, but revenue now includes parts of the supply chain and trading sectors, which are a relatively new venture. As per their publicly stated business operations and future direction, the Company's revenues should be divided into three categories:
- Semiconductor Chip Manufacturing– This is the largest single revenue segment for Polymatech. Polymatech's business model relies primarily on semiconductor chip manufacturing, and this segment will generate the most revenue.- The company manufactures semiconductor chips via wafer-level processing, assembly of microelectronics, and packaging of chips. Revenue from semiconductor chip manufacturing is directly associated with three specific factors: production volume, capacity utilisation, and the demand there is from Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) customers.
- LED Lighting Products - This is the secondary manufacturing segment of the Company. The Company leverages its materials science capabilities and manufacturing capabilities. The LED Lighting Products segment sees increased benefits from process optimisation and thermal management innovations, resulting from demand generated by industry, commercial, and infrastructure-linked markets. Although the demand for LED lighting products is less than the demand for semiconductor chips, it does give diversity to the electronics manufacturing sector.
- Using Manufacturing Technology with added value. Conducting revenue through embedded manufacturing. Polymatech will provide business infrastructure using embedded opportunities for advanced manufacturing within its current core business operations rather than as a separate reporting segment. The main focus will be on: Wafer-Level Packaging, Precision Automation, Ceramic Substrate materials with increased thermal conductivity, Devices, sensors, or other areas of specialisation within the electronics industry. These advances in manufacturing will provide Polymatech the ability to increase the overall value of products through higher ASP, improved customer relationships and the ability to provide more profitable margin quality.
- Trading/importing/exporting semiconductor/electronics components. Polymatech will establish an additional segment focusing on trading and the movement of equipment and components relating to semiconductors (e.g., chips, PCBs, substrates, capital equipment, tools, consumables, and software), on an international basis. This new segment will support Polymatech's existing manufacturing business by providing better control of the supply chain and quicker delivery of customer orders. Over time, this segment will allow Polymatech to change the distribution of revenues and partially mitigate the cyclic nature of its manufacturing business.
- Technology-Driven Manufacturing Optimisation - Polymatech has invested in AI Predictive Maintenance and IoT Energy Management through Digital Twin Technology; this will not create revenue on its own. However, Technology-Driven Manufacturing Optimisation has a significant effect on Cost Efficiency, Uptime, Yield Enhancement, and Operating Margins of all the Manufacturing Segments. By increasing Operating Leverage and enhancing Capital Return, Technology-Driven Manufacturing Optimisation will produce positive returns in the Medium to Long-Term.
Financial Performance
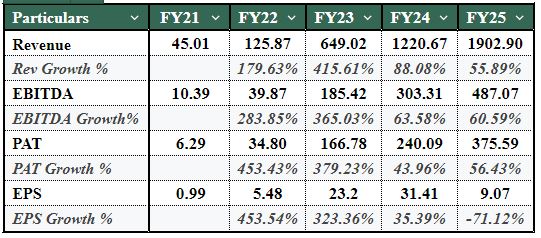
- Polymatech Electronics Limited has seen exceptional top-line revenue growth between the years of financial year FY2022 and FY2024 as a result of growing through scale expansion. From a relatively minor component manufacturing facility, Polymatech has transitioned to being a large semiconductor manufacturer in almost two years. From FY2022 to FY2024, revenue from operations rose from ₹126 crore to ₹1,221 crore – almost a tenfold increase in just two years. The primary driving force behind this explosive growth was the high volume of global demand for semiconductors and LED-related products, combined with the rapid expansion of their manufacturing facilities, the introduction of higher value products such as wafers, sapphire ingots and advanced semiconductor components into their portfolio of offerings, and increased cooperation with the OEM and export-based supply chains. Collectively, this period of time shows hyper-growth driven by the scale-up rather than an organic growth pattern.
- Nevertheless, while the overall amount of revenues earned is significant, growth was primarily driven by volume, based on increased production capabilities and the expansion of Polymatech's overall product portfolio, rather than by increases in pricing or profit margins. There appears to be a correlation between revenue growth and the ramp-up of new production capabilities, as well as the company's ability to handle that ramp-up effectively. Revenue is sensitive to the amount of capacity utilised, yield stability, and the consistency of OEM demand. While the overall growth profile of Polymatech is impressive, the extreme level of growth being experienced must be maintained by implementing strict operational control measures to ensure that margins are protected and sustained over time.
- Emerging Margin Pressure with Increasing Profitability - While total profitability increased significantly in this timeframe, margins were pressured when the organisation rapidly expanded. After-tax profit increased from ₹167 crore in FY2023 to ₹240 crore in FY2024; however, the PAT margin fell between FY2023 and FY2024 from a high of 25.7 per cent to 19.4 per cent. This suggests that the company's expenses increased at a quicker rate than its revenue during the most intense period of expansion and indicates the financial implications of a business growing rapidly.
- Expanding Margin Compression from Costs Associated with Scaling - The reduction in margins appears primarily to be structural and not attributed to demand, but rather to costs associated with the process of expansion. Some of the items that were a major contributor to this decline included the costs associated with logistics, energy, maintenance, compliance, test runs, and overhead associated with scale; increased costs for property, plant, and equipment resulting in higher depreciation costs; and additional employee costs because of the higher skill level needed for their more advanced manufacturing function; all these costs were recognised before achieving the company’s maximum potential for capacity and, as a result, led to temporary reductions in profit margins.
- Asset Investment and Asset Utilisation - Polymatech has made significant investments in fixed assets to create long-term manufacturing capabilities. Fixed assets at the end of the 2023 financial year were ₹154 crore, while they increased to ₹446 crore in 2024. While Polymatech's capital expenditures would lower asset productivity in the short term, as indicated by fixed asset turnover falling from 5.3 to 4.1, this trend indicates that the company has not yet achieved optimal utilisation of its newly added assets. Therefore, the revenue that Polymatech is currently realising is behind the amount of capital the company has invested, creating increased pressure on the company's return until optimal utilisation is attained. This delay in revenue realisation will create a heightened level of investment risk for a company that is scaling up to a larger industrial operation.
- Intensifying Working Capital Requirements - With aggressive growth patterns, Polymatech has significantly increased its cash requirements for day-to-day operating activities. During this period, the company's rising inventory levels were a result of stocking up to support expected sales in the future, as well as the development of new product lines. In addition, the rising levels of trade receivables directly resulted from the extended payment terms extended to OEM customers. Due to this, Polymatech has had to increase its use of working capital by 350% over the past 12 - 18 months. Working capital, which includes cash, inventory, and receivables, now takes more time to convert back into cash than ever before. The number of inventory days has increased from 23 to 76, and the number of days to collect trade receivables has increased from 45 to 98. This increased time to convert working capital back into cash means a longer cash conversion cycle and, therefore, requires a significant amount of internal cash to fund operations despite strong earnings being reported.
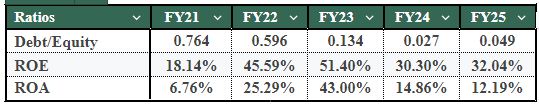
- Equity Contributions, Strength of the Balance Sheet, and Equity Dilution - In order to finance increases in capital expenditure and additional working capital needs, Polymatech has accessed equity markets through private placements in the manner prescribed, whilst concurrently making repayments to support a return to nearly zero leverage on the balance sheet. This has resulted in the company having a stronger balance sheet and lower financial risk, but it has also diluted earnings per share significantly. This dilution is most apparent for the FY2025 year, which may explain why Polymatech has continued to grow in absolute profits, yet has decreased earnings per share
- Conservative Capital Structure: Implications for Returns - Polymatech's capital structure is currently conservative, with a debt-to-equity ratio of approximately 0.03x. The impact of this conservative structure reduces the overall financial risk of the business while increasing management's focus on operational performance. Using an ROE and ROA perspective, return ratios declined in FY2024 and FY2025 due to increases in the equity base and limitations in the utilisation of capital assets. Therefore, future returns will depend more on the efficiency and effectiveness of operations than on financial leverage.
- Return Ratios Normalised During Expansion - Polymatech's return on equity and ROA were the highest in earlier years and have since declined through FY2024 through FY2025, driven by rapid growth in its asset base and concurrent increases in its equity base. In addition, some new facilities are not being fully utilised. This pattern illustrates the common timing mismatch for capital-intensive manufacturing organisations, with no deterioration in profitability.
Future Forecast with Assumptions
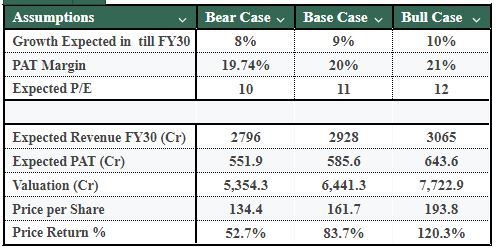
Assumptions
- Revenue Growth: For FY2025 - FY2030, we expect revenues for Polymatech to grow by roughly 8% (bear), 9% (base), and 10% (bull) CAGR, which corresponds to projected global opto-semiconductor market growth, with our bullish scenario resulting from scale and increasing market share.
- PAT Margin: Regardless of the business climate, we believe profitability will remain strong & continue to improve at a reasonable rate; we forecast 19.7% (bear), 20.0% (base), & 21.0% (bull) PAT margins. This projection is supported by increased leverage, improved efficiencies, and increased contributions of recurring and value-added revenues.
- Valuation Multiple (P/E): Our valuation for the company is based on a multiple of 10x (bear), 11x (base), & 12x (bull) P/E across the 3 different valuation scenarios; this represents varying levels of investor confidence in earnings sustainability, margin stability & execution consistency
Outcome
- Revenue Forecast: Projected revenues for Polymatech will be ₹2,796 crore in the bear case, ₹2,928 crore in the base case, and ₹3,065 crore in the bull case by FY2030, based on the above growth assumptions—indicating continued growth on a normal basis after the hyper-scale growth phase.
- Profitability Forecast: Estimated total earnings (PAT) are ₹551.9 crore (bear), ₹585.6 crore (base), and ₹643.6 crore (bull) by FY2030, based on the projected PAT margins—signifying continued improvement in operating leverage and a better capacity to absorb fixed costs as assets are being utilised efficiently.
- Valuation Projections: The implied valuation of Polymatech's equity is projected at ₹5,354 crore (bear), ₹6,441 crore (base), and ₹7,723 crore (bull) when applying the corresponding P/E multiples—showing the range of estimated equity values based on growth visibility and profitability expectations.
- Value per Share: The valuations translate into estimated per share prices of ₹134.4 (bear), ₹161.7 (base), and ₹193.8 (bull)—illustrating the sensitivity of equity value to small changes in growth, PAT margins, and valuation multiples within the range of valuations.
- Return on Investment: The expected return on investment from current market prices will be 52.7% (bear), 83.7% (base), and 120.3% (bull)—demonstrating a strong positive risk-return profile if the execution strategy continues to be successful.
- The analysis indicates that medium-term success and further growth for Polymatech's business hinge on the company's earnings base and sufficient operating leverage. The Bull Case further highlights the possibility of Polymatech receiving a greater valuation by continuing to manage margins, create cash-flow stability, and maintain consistent utilisation levels of its increased manufacturing capabilities.
Peer Comparison
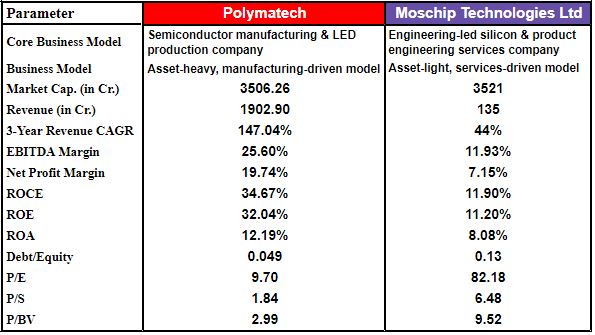
- MosChip Technologies Limited and Polymatech both compete within the same semiconductor value chain. However, they are positioned within the value chain in entirely different segments. They have different business models as well (i.e., Polymatech is an asset-intensive model in semiconductor manufacturing and LED production, while MosChip operates with a low asset base, engineer-driven model in silicon and product engineering).Due to these two unique positions, the two companies have a fundamental divergence in growth, profit margins, capital efficiency, and financial metrics (valuation).
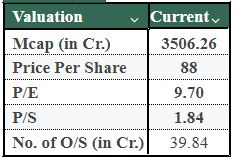
- Polymatech is considerably larger than MosChip on an operational basis. In particular, for the period ended March 31, 2023, Polymatech reported revenue of Rs.1,902.9 crore vs. Rs.135 crore for MosChip, while both companies have similar total market capitalisation (approximately Rs.3,500 crore). Therefore, this tells us that Polymatech has a much larger manufacturing base than MosChip has a smaller revenue profile, however, because there are more multiples associated with service business models (like those of MosChip) than with manufacturing models, they equalise in terms of total market capitalisation,
- Polymatech is experiencing much more rapid growth than MosChip, with a revenue CAGR of 147.0% vs. 44% for MosChip over the last three years. Polymatech is rapidly expanding its capacity and entering more valuable semiconductors, while MosChip's growth is slower, incremental, and project-driven.
- Polymatech outperforms MosChip with regard to key profitability metrics (generally accepted methods of measuring profitability). At the operating level, for example, Polymatech has an EBITDA margin of 25.6% compared with 11.9% for ~MosChip, and a Net profit margin of 19.7% compared with 7.2% for MosChip. While Polymatech earns its high margins based on the scale of its manufacturing facilities and the risks involved in using manufacturing facilities (utilisation), the operating leverage that Polymatech has in terms of its margin indicates that, at this time, Polymatech has greater potential to grow than does MosChip due to the higher percentages associated with manufacturing than with services.
- Polymatech's return metrics show that it has higher returns on capital employed (ROCE) and return on equity (ROE) than MosChip, with Polymatech having a ROCE of 34.7% and ROE of 32.0% compared to the company's ROCE of 11.9% and ROE of 11.2%. This indicates that Polymatech is currently more adept at utilizing its capital as it continues its scale-up. In addition to the differences in ROCE and ROE between the two companies, it should be noted that the ROA for Polymatech is at 12.2%, which is only moderately higher than MosChip's ROA of 8.1%, as the manufacturing industry typically has a heavier asset base than companies in other industries.
- In terms of their balance sheets, both Polymatech and MosChip maintain relatively low levels of leverage; however, Polymatech has lower amounts of debt than MosChip, which is reflected in its debt/equity ratio of 0.049 vs. 0.13 for MosChip. This indicates that Polymatech is financially stronger than MosChip, but while Polymatech depends heavily on operational execution to achieve return on equity (ROE), MosChip relies more on utilizing its equity to gain returns.
- The valuation metrics for Polymatech and MosChip indicate a stark contrast in the market's outlook for both companies. Polymatech is trading at a P/E of 9.7x and P/S of 1.84x, whereas MosChip is trading at P/E of 82.2x and P/S of 6.48x. The large discrepancy in the price/earnings ratios indicates that the market is giving MosChip a premium over its earnings, about the sustainable nature of low-capital-intensive service-based companies, while the capital-intensive manufacturing operations of Polymatech place a high level of risk on their operations and make them very susceptible to cyclical fluctuations.
- Overall, the peer comparison indicates that Polymatech is valued more like a capital-intensive industrial manufacturer despite its superior growth and profitability metrics, whereas MosChip is priced as a high-multiple engineering services company. Polymatech’s investment case, therefore, hinges on successful utilization of its expanded manufacturing base and sustained margin stability, which could narrow the valuation gap relative to asset-light peers over time.
Key Risks
While operating from a structurally growing segment of the semiconductor space, the company's expectations for growth will depend upon several internal execution and external factors. That means that:
- Capital and Execution Risks: Continuous need for capital investments into advanced semiconductor manufacturing equipment and clean-room infrastructure. Delays in obtaining that capital, greater-than-expected costs, and/or failure to deploy capital efficiently will all cause Polymatech to have less favourable returns and will slow the growth of capacity.
- Technology Obsolescence: The speed of innovation and advancement in semiconductor packaging, materials, and automation is so great that Polymatech will need to upgrade technology on a continuous basis in order to remain competitive and maintain product margins.
- Supply Chain and Dependency on Imported Components and Speciality Materials: Continued reliance on imported equipment and specialty materials will expose Polymatech to geopolitical issues, regulatory restrictions, and currency volatility.
- Governance Risks: Recent changes in key board committees due to director resignations may have temporarily increased Polymatech's governance and compliance risks at a critical period of growth.
- Customer Concentration Risks: Long OEM qualification cycles and possible reliance on a small base of customers will reduce the company’s revenue visibility for the near-term.
Future Growth Driver
- Many of the structural trends that are driving demand for Polymatech (i.e. EVs, AI, industrial automation, renewable energy and medical electronics combined with government initiatives to localise semiconductor manufacturing) will help expand the company's addressable market.
- Polymatech's vertical integration strategy will allow the company to expand into trading and supply chain services thus enabling the company to become a much more comprehensive player within the electronics ecosystem, thereby allowing for greater resilience, improved margins and maximised customer engagement.
- Polymatech's adoption of advanced manufacturing techniques (i.e. through the use of AI-driven maintenance, digital twins and automation) will enable the company to produce at scale with high-yield, thus allowing for entry into high-reliability applications.
- Polymatech's international presence as well as its strategic vision allow the company to leverage its global platform through market access and diversification opportunities through the use of multiple business models with strategic optionality across multiple manufacturing, export and policy-supported semiconductor programme opportunities.
Conclusion
Polymatech Electronics is a semiconductor manufacturer with a heavy capital expenditure commitment, aligned with the Indian Government's localisation agenda (i.e. manufacturing locally), utilising the benefits from scalability and vertical integration in manufacturing, as well as diversifying into new markets like Medical Device Technologies and GaN Chip manufacture. However, the elevated risk of execution in the near future, the reliance on a high percentage utilisation to drive profitability, and a limited amount of short-term visibility for profitability, suggest that the stock could be valued more in the fairly and slightly aggressive range than being valued as clearly undervalued. This stock is therefore suitable primarily for long-term investors with a higher risk tolerance and the ability to execute a longer-term strategic investment plan with a higher level of risk. This stock is not suitable for short-term investors or conservative investors. This share is available for investment through SharesCart.






